Ecuador – Country Profile
General Information
| Official Name | Republic of Ecuador |
| Capital | Quito |
| Total Area | 283, 561 sq km |
| Population | 15 million (July 2014 estimate) |
| Currency | 1 CAD = 0.92 United States Dollars (USD) (20/05/2014) |
| National Holiday | August 10 (Independence Day) |
| Language(s) | Spanish, Quechua, Shuar |
Source: Economic Intelligence Unit, Bank of Canada (Currency Conversion 05/20/2014)
Political Information
| Type of State | Republic |
| Head of State | President Rafael Correa Delgado (since January 2007) |
| Elections | Last: February 2013 Next: 2017 |
Source: Economic Intelligence Unit
Economic Information
| Ecuador | Canada | |
| GDP (PPP) | $171 billion | $1,878 billion |
| GDP per capita | $11,555 | $53,518 |
| GDP annual growth rate | 4% | 2.01% |
| GDP – composition by sector | Agriculture: 5.9%
Industry: 35.1% Services: 59% |
Agriculture: 1.7%
Industry: 28.4% Services: 69.9% |
| Inflation rate | 2.6% | 0.96% |
| Main industries | Petroleum, food processing, textiles, wood products, and chemicals | Transportation equipment, chemicals, processed and unprocessed minerals, food products, wood and paper products, fish products, petroleum and natural gas. |
Note: 2013 data in Canadian dollars ($CAD)
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook, World Bank Data, CIA World Factbook, Bank of Canada (Currency Conversion 06/06/2014)
Political and Economic Stability
In 2000, Ecuador adopted the United States Dollar (USD) as legal tender, and structural reforms were introduced to improve economic stability. However by 2008, Ecuador was forced to default on its commercial bond obligations due to a decline in foreign investment and low oil prices. As oil prices regain their strength, so too has the Ecuadorian economy, reaching GDP growth of 8% in 2011 and 5% in 2012. Now that large reserves of gold, copper, titanium and other metals have been discovered in Ecuador, the economy is expected to remain strong.
The election of Rafael Correa in 2007 has also helped bring stability to the region. Ruling for a third consecutive term, Correa has invested heavily in social programmes and infrastructure, dropping poverty rates by 10% in 5 years. In order to fund this social spending, Ecuador has been borrowing heavily from China.
Canada and Ecuador have signed a double taxation treaty as well as a Foreign Investment Protection Agreement (FIPA). While it is important to note that Ecuador has unilaterally withdrawn from several foreign investment protection agreements, the Canada-Ecuador agreement currently remains in effect.
Security
In terms of security, the Department of Foreign Affairs, Trade and Development Canada (DFATD) recommends that Canadians exercise a high degree of caution when traveling in Ecuador. While there is no nationwide advisory in effect, DFATD advises against all travel to areas immediately bordering Colombia due to the presence of drug traffickers and criminal organizations. For detailed and up-to-date information on travel security, please refer to the DFATD Travel Report for Ecuador.
Trade Information
| Trade Partners & Direction | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | Ave. Yearly Growth |
| Ecuador Exports to the World | $15,748 M | $18,012 M | $22,079 M | $23,838 M | $25,655 M | 13% |
| Ecuador Exports to United States | $5,255 M | $6,259 M | $9,611 M | $10,656 M | $11,426 M | 23% |
| Ecuador Exports to Canada | $234 M | $215 M | $225 M | $262 M | $294 M | 6% |
| Canadian Exports to Ecuador | $269 M | $263 M | $281 M | $265 M | $303 M | 3% |
Note: Data in millions of Canadian dollars ($CAD)
Source: Trade Data Online (Industry Canada), Trade Map (International Trade Centre), World Integrated Trade Solution (World Bank), United States Trade Representative
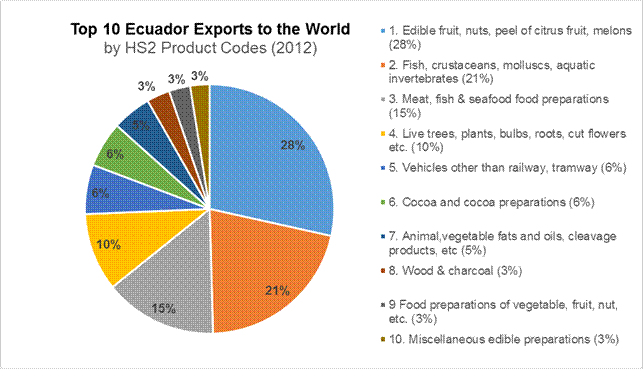
Excluding mineral products (HS2 Codes 26-27 and 71-80)
Source: International Trade Centre Trade Map
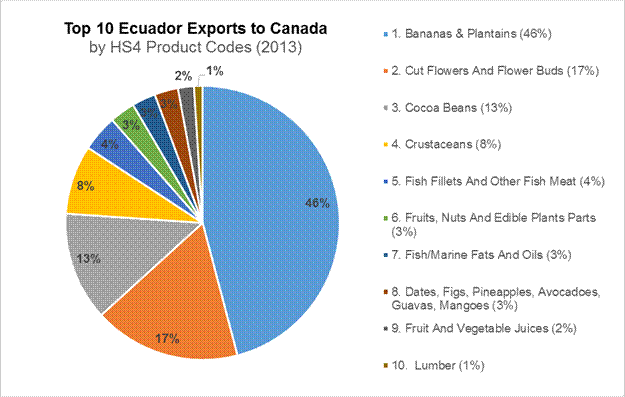
Excluding mineral products (HS2 Codes 26-27 and 71-80)
Source: Industry Canada Trade Data Online
Business Climate
The World Bank’s annual Doing Business report ranks economies from 1 to 189 (with 1 being the best) on their ease of doing business. In the 2014 report, Ecuador ranked 135 overall and 122 for Trading Across Borders, which measure the ease with which a standardized shipment of goods can be imported or exported across its borders. The average time to ship goods out of Ecuador is slightly longer than the regional average at approximately 20 days, with an average estimated cost of $USD 1,535 per 20-foot container. To complete the export process, seven forms of documentation are required: Bill of lading, Commercial invoice, Customs export declaration, Equipment interchange receipt, Insurance certificate, Packing list, and Technical standard/health certificate.
Although there are many reputable exporters in Ecuador, Canadian importers should be aware that corruption could be an issue when doing business in the country. Ecuador ranked 102 out of 177 in Transparency International’s 2013 Corruption Perceptions Index where 1st place indicates least corrupt. Canadian companies are advised to exercise strict due diligence before working with a company from Ecuador to ensure that it is a bona fide and reputable entity. It is suggested that Canadian importers commission a report by a credit information provider to verify the financial strength of the partner.
Trade Opportunities
Ecuador depends highly on its petroleum exports, which constitute more than half of total export earnings. Nevertheless, Ecuador is one of the world’s most bio-diverse countries, containing several microclimates, which allows it to provide a wide range of products that are in high demand amongst North American consumers. Among Latin American countries, Ecuador is Canada’s number one cocoa exporter, making gains of 300% from 2012 to 2013. It is also the second largest Latin American exporter to Canada of fish, crustaceans, and molluscs, live trees, plants, and cut flowers; it is the fourth for edible fruit and nuts. As the world’s largest banana exporter as of 2011, 36% of Ecuador’s exports to Canada comprise of bananas and plantains. Another 14% of its exports to Canada are cut flowers.
Ecuador has a wide variety of fruits and vegetables to offer Canadian importers. The high quality of produce and year-round available supply makes Ecuadorian produce very attractive to Canadian importers. The most popular fruit exports are bananas, guavas, mangoes, passion fruit, papaya, and pineapple. There is significant opportunity to expand Canadian imports of these products, while expansion of baby banana, pitahaya, lime, physalis and watermelon crops provide new opportunities for Canadian importers. In recent years, Ecuadorian farmers have been greatly increasing their production of organic produce, especially bananas. In terms of vegetables, the most promising trade opportunities include hearts of palm, broccoli, and asparagus. Ecuador also produces various processed fruit and vegetable products which are available in several forms, including: dehydrated, powder, flakes, flour, jellies, chips and chocolate-covered.
Import opportunities exist for a variety of other Ecuadorian agricultural products. For several decades, cocoa was Ecuador’s primary export. Today the country exports a variety of cocoa by-products and is known as the world’s primary producer of extra fine cocoa, whose rich, one of a kind flavour and floral aroma make it unique worldwide. Ecuador also produces a variety of coffee and coffee extracts, including specialty and gourmet coffees, in the categories of organic, fair trade, and of origin. Other growing areas of opportunity include medicinal and aromatic herbs and a variety of gourmet food products.
Ecuador is the world’s third largest exporter of flowers and the second largest exporter of roses. Main varieties now available to Canadian importers include: gypsophila, summer flowers, tropical flowers and orchids.
Already one of the top Ecuadorian products sought out by Canadian importers, Ecuador’s tilapia, tuna and shrimp stocks are amongst the largest in the world. New areas of opportunity for fresh and processed fish include rainbow trout, and Chame fish; a sweet water farmed fish unique to Ecuador. All varieties are available for export in fresh, frozen, canned or fishmeal forms.
Ecuador’s talented artisans make use of an extensive selection of natural materials including wood, leather, ceramic, and a variety of natural fibres to craft home décor items and household furniture. Similarly, these natural materials are used to produce clothing, accessories and other household textiles. One of the most rapidly growing export sectors is high value-added forest products where the greatest interest to Canadian importers lies in balsa and teak wood doors, furniture, windows and floors.
Finally, the manufacturing sector in Ecuador has taken off in recent years. Ecuadorian companies possess the technical know-how necessary to manufacture metal components, machinery, equipment and related inputs for numerous uses. Likewise, the Ecuadorian automotive industry specializes in parts and vehicle assembly.
TFO Canada Export Offers
TFO Canada provides an information service for Canadian importers interested in sourcing products from developing and emerging economies such as Ecuador. This includes practical advice on sourcing from developing country exporters, a customized news bulletin including new leads from the Ecuador as they come in, and a searchable database for sourcing new products and suppliers. The chart below provides a rough idea of the number of Ecuador supplier profiles, available online with contact information through TFO Canada’s searchable Supplier Database.
| Industry Group | No. of Suppliers in TFO Database |
| Food products and beverages (incl. seafood) | 18 |
| Clothing (not including footwear) | 3 |
| Floriculture | 2 |
| Building Materials, Hardware and Hand tools | 2 |
| Animals and Animal Based Products | 2 |
| Fashion Accessories | 1 |
| Professional and Other Services | 1 |
Upcoming Trade Shows
Construyendo & Decorando
August 20-24, 2014
Centro de Convenciones de Guyaquil, Guayaquil, Ecuador
Industries: Building Construction & Décor
http://10times.com/construyendo-decorando
Agriflor Holland
22-25 September, 2014
Quito Centro de Exposiciones, Quito, Ecuador
Industries: Floriculture & Gardening
Flower and plant collections, floristry supplies, floral arrangements, floral decorations, flowerpots and window boxes, earthenware
http://tradeshow.tradekey.com/agriflor-holland-e8529.htm
Agriflortec
24-26 September, 2014
Quito Centro de Exposiciones, Quito, Ecuador
Industries: Floriculture & Gardening
Flower and plant collections, floristry supplies, floral arrangements, floral decorations, flowerpots and window boxes, earthenware
http://tradeshow.tradekey.com/agriflortec-e689.htm
Florecuador – Agriflor
October 1-4, 2014
Quito Centro de Exposiciones, Quito, Ecuador
Industries: Floriculture & Gardening
Soil softeners, lawn-mowers, watering equipment, hoses, saws, clippers, spades, rakes, wheelbarrows, nets, foils, greenhouses, awnings, vases, composts, fertilisers, grass, seeds, flowers, ornamental plants, herbicides, insecticides
http://www.hppexhibitions.com/floriculture/2014/ecuador
Expo Belleza
October 24-27, 2014
Centro de Convenciones de Guyayaquil, Guyaquil, Ecuador
Industries: Cosmetics & Beauty, Fashion, Health
Products related to fashion and beauty, salons, spas and medical, living and healthy eating, cosmetics, personal care and skin, cam natural products, clothing and accessories
http://10times.com/expo-belleza
Cumbre Mundial De Banano
November 10-12, 2014
Guyaquil, Ecuador
Industries: Agriculture (Bananas)
Agrochemicals suppliers, importers of agricultural inputs, fumigation, fertilizer, packaging materials, irrigation systems and transportation, machinery and tools suppliers
http://10times.com/cmb
Contact Information
Embassy of Ecuador in Canada
99 Bank, Suite 230, Otatwa, ON K1P 6B9
Tel.: (613) 563-8206 / (613) 563-4286
Email: embassy@embassyecuador.ca
Website: www.embassyecuador.ca
Pro Ecuador Office in Canada
130 Adelaide Street West, Suite 2101, Toronto, ON M5H 3P5
Tel.: (647) 352-5511 / (647) 352-5512 / (647) 825-8857
Email: msilvav@proecaudor.gob.ec
Website: www.proecuador.gob.ec (Spanish only)
Useful Links
| CORPEI (Non-profit Export and Investment Promotion Corporation of Ecuador) | www.corpei.org (Spanish only) |
| FEDEXPOR (Federation of Ecuadorian Exporters) | www.fedexpor.com/index.php(Spanish only) |
| Ministerio de Relaciones Exteriores, Comercio e Integración (Ecuador Ministry of External Relations, Commerce and Integration) | http://www.mmrree.gob.ec/eng/ |
| Ministerio de Turismo del Ecuador (Ministry of Tourism) | http://www.turismo.gob.ec/ (Spanish only) |
| Pro Ecuador (Ecuador’s Export and Investment Promotion Agency) | www.proecuador.gob.ec (Spanish only) |
| Superintendencia de Compañías del Ecuador (Superintendent of Ecuadorian Companies) | www.supercias.gob.ec/ (Spanish only) |
| Trade Commission of Ecuador to Canada, Toronto | www.embassyecuador.ca/english/index.php?id=comercial&nro=1 |
Links to Cited Documents
| Bank of Canada – Daily Currency Convertor | http://www.bankofcanada.ca/rates/exchange/daily-converter/ |
| Canadian Trade Commissioner Service – Country Info | http://www.tradecommissioner.gc.ca/eng/trade-offices.jsp |
| CIA World Factbook | https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/ |
| DFATD (Department of Foreign Affairs, Trade & Development) – Foreign Relations | http://www.international.gc.ca/cip-pic/geo.aspx |
| DFATD (Department of Foreign Affairs, Trade & Development) – Travel Reports | http://travel.gc.ca/travelling/advisories |
| EDC (Export Development Canada) – Country Profiles | http://www.edc.ca/EN/Country-Info/Pages/default.aspx |
| Industry Canada – Trade Data Online | https://www.ic.gc.ca/eic/site/tdo-dcd.nsf/eng/Home |
| International Trade Centre – Trade Map | http://www.trademap.org/ |
| Transparency International – Corruption Perception Index | http://cpi.transparency.org/cpi2013/results/ |
| World Bank – Doing Business Report | http://www.doingbusiness.org/rankings |
| World Bank – Open Data | http://data.worldbank.org/country |
